Fingerstyle guitar is a versatile and expressive technique that allows guitarists to play melody, harmony, and rhythm simultaneously. Whether you’re drawn to the intricate patterns of Travis picking or the elegance of classical fingerstyle, mastering these techniques can greatly enhance your musicality. This guide delves into various fingerstyle techniques, offering detailed insights and practice tips to help you become a proficient fingerstyle guitarist.
1. Basics of Fingerstyle Guitar
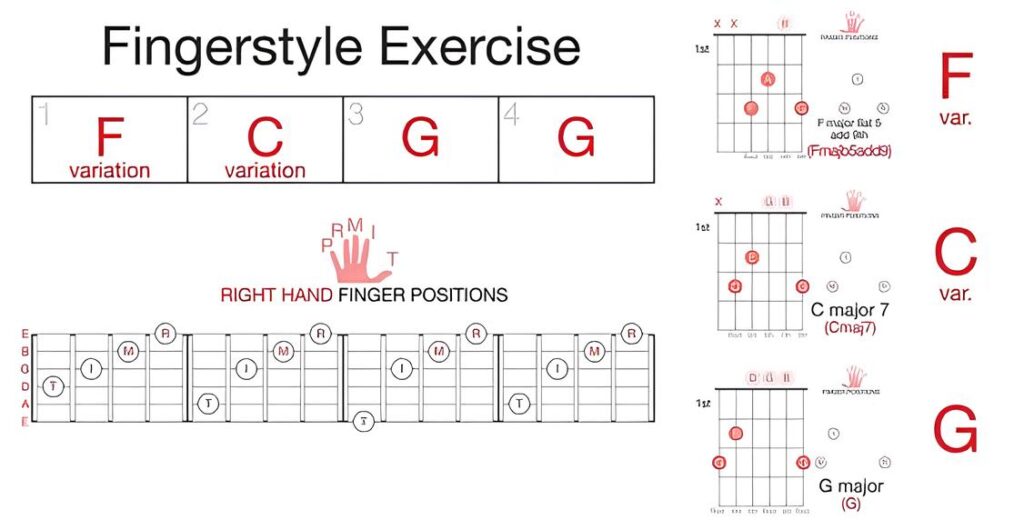

Finger Positioning:
- Thumb (P): Used for the bass notes on the E, A, and D strings.
- Index (I): Typically plucks the G string.
- Middle (M): Typically plucks the B string.
- Ring (A): Typically plucks the high E string.
Basic Patterns:
- Start with simple patterns, such as alternating thumb and finger strokes. For example, a basic fingerstyle pattern on a C major chord might look like this:
e|-------0-------|
B|----1----------|
G|--------0------|
D|-------------2-|
A|--3------------|
E|---------------|2. Travis Picking


Overview:
Travis picking, named after country guitarist Merle Travis, is a fingerpicking style where the thumb alternates between bass notes while the fingers play melody notes. This technique creates a steady, rolling rhythm that is common in folk, country, and blues music.
Technique:
- Thumb Alternation: The thumb alternates between two bass strings, typically the root and the fifth of the chord.
- Syncopation: The fingers pluck melody notes in a syncopated rhythm, often emphasizing the off-beats.
Pattern Example:
- A common Travis picking pattern on a C major chord:
e|-------0-------|
B|----1----------|
G|--------0------|
D|---------------|
A|--3------------|
E|---------------|
Thumb: A-D-A-D (alternating)
Fingers: I (G string), M (B string), A (high E string)Practice Tips:
- Start Slow: Begin with a metronome at a slow tempo to develop coordination between the thumb and fingers.
- Isolate Movements: Practice the thumb movement independently until it becomes automatic, then add the finger movements.
- Syncopation Focus: Emphasize the syncopated rhythm by accentuating the off-beats with your fingers.
3. Classical Fingerstyle
Overview:
Classical fingerstyle is rooted in classical guitar tradition, focusing on precision, tone, and technique. It involves intricate finger movements and often uses nylon-string guitars for their warm, resonant sound.
Technique:
- Finger Independence: Each finger (P, I, M, A) operates independently, often plucking different strings simultaneously.
- Arpeggios and Scales: Classical fingerstyle frequently involves playing arpeggios and scales with smooth, even tones.
- Rest Stroke (Apoyando) and Free Stroke (Tirando): Two primary plucking techniques. Rest stroke involves plucking a string and letting the finger rest on the next string, while free stroke involves plucking without touching the next string.
Pattern Example:
- A simple classical arpeggio pattern on an E minor chord:
e|-----------0-----|
B|-------0---------|
G|-----0-----------|
D|---2-------------|
A|-------------2---|
E|-----------------|
Thumb: E, A, D strings
Fingers: I (G string), M (B string), A (high E string)Practice Tips:
- Finger Independence Exercises: Practice exercises that isolate each finger to develop independence and strength.
- Tone and Dynamics: Focus on producing a clear, even tone and experiment with dynamics to add expression to your playing.
- Use a Metronome: Maintain a steady tempo and gradually increase the speed as you become more comfortable with the patterns.
4. Hybrid Fingerstyle
Overview:
Hybrid fingerstyle combines traditional fingerstyle with plectrum (pick) playing. This technique allows for versatile playing, combining the precision of fingerpicking with the power of flatpicking.
Technique:
- Pick and Fingers: Hold a pick between your thumb and index finger while using your middle, ring, and pinky fingers for plucking.
- Alternate Between Pick and Fingers: Use the pick for bass notes or strumming and the fingers for melody or arpeggios.
Pattern Example:
- Hybrid picking on a G major chord:
e|-------3-------|
B|-----0---------|
G|---0-----------|
D|---------------|
A|--2------------|
E|---------------|
Thumb (pick): E, A, D strings
Fingers: M (G string), A (B string)Practice Tips:
- Develop Coordination: Practice switching between pick and fingers smoothly.
- Balance Sound: Ensure the pick and fingers produce a balanced sound, neither overpowering the other.
- Use in Various Styles: Experiment with hybrid fingerstyle in different genres, from rock to folk to jazz.
5. Percussive Fingerstyle
Overview:
Percussive fingerstyle incorporates rhythmic tapping, slapping, and other percussive elements into the fingerstyle technique. This style is popularized by modern acoustic guitarists like Andy McKee and Tommy Emmanuel.
Technique:
- Tapping: Use your fingers to tap on the fretboard, producing hammer-ons and pull-offs.
- Slapping: Use the thumb or palm to slap the strings or guitar body, creating a percussive sound.
- Harmonics: Combine natural and artificial harmonics with percussive elements for a unique sound.
Pattern Example:
- Percussive tapping on a D chord:
e|---------------|
B|---3h5p3-------|
G|--------2h4p2--|
D|---------------|
A|---------------|
E|---------------|Practice Tips:
- Rhythmic Precision: Focus on keeping a steady rhythm, incorporating percussive elements in time with the music.
- Explore Techniques: Experiment with different percussive techniques to find what works best for you.
- Combine with Melodies: Practice integrating percussive elements with melodic lines and chords.
6. Flamenco Fingerstyle
Overview:
Flamenco fingerstyle, originating from Spain, is known for its rapid, rhythmic, and dynamic strumming and plucking techniques. This style often employs the use of the rasgueado (strumming with the fingers) and alzapúa (thumb technique).
Technique:
- Rasgueado: Strum with the backs of the fingers in a rapid, rolling motion.
- Alzapúa: Use the thumb for rapid, repetitive downstrokes, upstrokes, and plucking.
- Picado: Rapid, alternating plucking with the index and middle fingers.
Pattern Example:
- Rasgueado pattern on an A minor chord:
e|------------------|
B|------------------|
G|----2-------------|
D|----2-------------|
A|----0-------------|
E|------------------|Practice Tips:
- Develop Speed and Accuracy: Practice rasgueado and alzapúa slowly, gradually increasing speed while maintaining accuracy.
- Finger Strength: Focus on building finger strength and endurance for rapid strumming and plucking.
- Explore Flamenco Rhythms: Study traditional flamenco rhythms, such as bulerías and soleá, to understand the context of the techniques.

Conclusion
Fingerstyle guitar techniques like Travis picking, classical fingerstyle, hybrid picking, percussive fingerstyle, and flamenco offer a wide range of expressive possibilities. Each technique has its unique characteristics and applications, allowing you to create intricate melodies, harmonies, and rhythms. By practicing these techniques diligently and incorporating them into your playing, you’ll expand your musical vocabulary and develop a versatile, expressive fingerstyle guitar repertoire. Happy playing!




- July 5th in America: The Quiet Day After the Boom
- Who Is Vanessa Trump? Inside the Life of Donald Trump Jr.’s Former Wife
- Remembering Steve McNair 16 Years Since the Titans Legend’s Tragic Passing
- Is Guitar Center Open on 4th of July? Here’s What You Need to Know
- Unlocking Style Core Aesthetics: The New Era of Personal Fashion

